Québec / Canada and the simplest satellite, the PS-1 spacecraft, in other words Sputnik 1: An overview of what was published in the French language Québec press between 5 and 12 October 1957, Part 1

Happy World Space Week 2020, my reading friend!
Would you believe that the first issue of our blog / bulletin / thingee came out 3 years, 3 months and 3 days ago? And yours truly is still digressing…
If you do not mind, I wish to abandon, for this week only, rest assured, the anniversarial format of our blog / bulletin / thingee in order to devote many pontificating lines to a question which, at least I hope so, has not been discussed very, very often: how the daily and weakly, sorry, weekly French language Québec press described what was being done and said in Canada and, more specifically, Québec, about the first artificial satellite, the Soviet Sputnik 1, mentioned several times in our blog / bulletin / thingee since February 2018. Given the sheer scope of the subject and a certain laziness on my part, I will limit this pontification to the 7 days following the launch of said artificial satellite. Pinky sworn.
With this introduction behind us, let’s take action, and…
You have a question, don’t you? That’s good. What do the expressions simplest satellite and PS-1 spacecraft mean, you ask? These were quite simply expressions commonly used in the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) to describe Sputnik I, and…
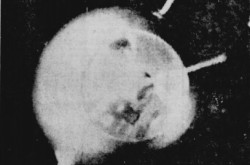
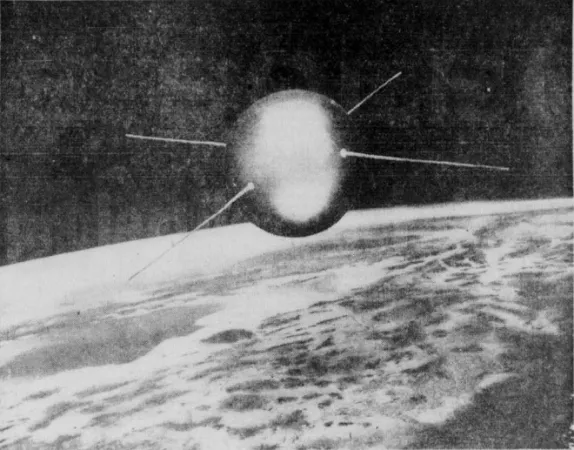
You have another question, don’t you? Sigh. Is the illustration at the beginning of this article a mere drawing? Um, let me give you a museum curator’s answer: yes and no. What you have seen, my reading friend, was / is a drawing by an unknown American artist which had been superimposed on a photograph of our good old Earth taken in February 1955 at an altitude of about 230 kilometres (approximately 145 miles) from the 12th and final Martin Viking rocket launched by the United States Naval Research Laboratory of the United States Navy.
Before you ask a third question, allow me to answer it. The Soviet artificial satellite launched in October 1957 circulates around the Earth at a much higher altitude, between 215 and 940 kilometres (approximately 135 to 585 miles) above sea level, which corresponded to an orbit duration of a little more 90 minutes, but back to our story.
As you can imagine, the launch of said Soviet artificial satellite, on 4 October 1957, hit like a bomb. This being said (typed?), the fact was that the Soviet government had announced its intention to place a satellite in orbit as early as July 1955. This placement was to be done within the framework of the International Geophysical Year, a period of time of approximately 16 months (July 1957 to December 1958) devoted to research work on Earth carried out on a world level mentioned in several issues of our blog / bulletin / thingee since July 2018.
By the way, do you remember that a Soviet astrophysicist mentioned in a September 2019 issue of our yadda yadda, Alla Genrikhovna Masevich, was put in charge of the optical observation team set up to keep an eye on said satellite?
Asked during the evening of 4 October, shortly after the announcement of the launch of the “first island of the ether,” the translation of an expression used by the Soviet press, at least that’s what La Presse, a major Montréal, Québec, daily, claimed, Dominion astronomer Carlyle Smith Beals said it would be easier to detect it using spy-glasses than with the large telescopes from observatories around the world, including the gargantuan reflector telescopes at the Dominion Astrophysical Observatory (185 centimetres / 73 inches in diameter mirror), in Saanich, near Vancouver, British Columbia, and the David Dunlap Observatory (188 centimetres / 74 inches) of the University of Toronto, in Richmond Hill, near Toronto, Ontario.
The large refractor and reflector telescopes being able to only scan a tiny portion of the sky at a time, the Dominion Observatory therefore intended to use small telescopes instead of its refractor telescope, the most powerful instrument of its kind in the country, an instrument whose lens measured no less than 38 centimetres (15 inches) in diameter.
And if you believe Canadian refractor and reflector telescopes were ginormous, let me mention the reflector telescopes at the McDonald Observatory (208 centimetres / 82 inch diameter mirror), in Texas, and the Mount Wilson Observatory (254 centimetres / 100 inches), in California. As for the refractor telescope of the Dominion Observatory, more than 50 observatories around the world had an instrument with a lens of a larger diameter.
Would you believe that said refractor telescope is now, in 2020, part of the collection of the Canada Science and Technology Museum, in Ottawa, Ontario – a sister / brother museum of the fantabulastic Canada Aviation and Space Museum, in Ottawa? A very personal opinion if may be permitted. Said refractor telescope should be on the site of this second museum. Astronomy as a whole should in fact be part of the research fields of the Canada Aviation and Space Museum. Just sayin’. (Hello, boss lady, hello!) But back to our story.
The aforementioned Beals also mentioned that, while the radio receivers at the Dominion Observatory probably could not pick up signals from the Soviet satellite, those of the National Research Council and the Department of National Defence probably could.
At least one reporter also interviewed Gustav Bakos, an assistant at the David Dunlap Observatory and a doctoral student in the Department of Astronomy at the University of Toronto, during the evening of 4 October. According to him, the Soviet satellite was moving at such a speed that only observers equipped with powerful spy-glasses were likely to see it, and again only at dawn and dusk. It was indeed at these times that the small metallic sphere was illuminated by the Sun.
It was / is fair to assume that the Dominion Observatory asked the personnel of all experimental stations and observatories which had adequate equipment to attempt to photograph the Soviet satellite. In fact, Arthur A. “Art” Griffin, the researcher in residence at the observatory in Newbrook, Alberta, an experimental station of the Stellar Physics Division of said observatory, seemed to receive such a request as early as 5 October, but let us continue our story.
At around 6.30 p.m., local time, on 4 October, a technician at the CHLT radio station, owned by La Tribune, the daily newspaper in Sherbrooke, Québec, yours truly’s homecity, picked up signals emitted by the Soviet satellite. This amateur radio operator managed to stay tuned for about 10 minutes.
At around 8:30 p.m., local time, an amateur radio operator, Martin Hansen of Edmonton, Alberta, managed to pick up signals from the satellite, which he said were very weak, for about 20 minutes.
At around 10 p.m., local time, it was reported that Douglas Johnson, an amateur radio operator from Halifax, Nova Scotia, had picked up radio signals from the Soviet artificial satellite. He recorded said signals and sent them to the local station of the Canadian state radio and television broadcaster, Canadian Broadcasting Corporation. Delighted, the management of CBHT broadcasted said signals during its newscast of 11:30 p.m., local time always.
Yet another amateur radio operator, Baden Langton of Hamilton, Ontario, heard signals transmitted from the satellite shortly before 11:30 p.m., local time. He lost contact after about 8 minutes. Interestingly, Langton became a television and radio news anchor in Canada and the United States during the 1960s.
The launch of the first artificial satellite played a mean trick for the management of a well-known Canadian aircraft manufacturer and subsidiary of British industrial giant Hawker Siddeley Group, A.V. Roe Canada Limited (Avro Canada) of Malton, Ontario. For several years, the Aircraft and Gas Turbine Divisions of this aeronautical giant, renamed Avro Aircraft Limited and Orenda Engines Limited in 1954-55, had been working on a supersonic bomber interceptor project intended for the Royal Canadian Air Force. The CF-105 Arrow program reaches a milestone on… 4 October 1957. More than 12 000 people attended the unveiling of the first aircraft at the Avro Aircraft factory. Management was delighted; the Arrow would make the front page of Canada’s most important dailies. As we now know, luck dictated otherwise. The headlines went to the Soviet satellite.
Is it necessary to mention that Avro Canada and Hawker Siddeley Group have been mentioned several times in our blog / bulletin / thingee since March 2018? No? Very well.
The launch of the first artificial satellite obviously made headlines in the French language Québec dailies of 5 October, but not necessarily on the front page. If a major daily, La Patrie of Montréal, for example, stated on its front page, in translation, “Satellite launched by Russia,” the large article containing information on the “Earth satellite launched by Russia” was relegated to the page 18. A respectable conservative daily in Québec, Québec, L’Action catholique, for its part, informed its readership, in translation, that “Moscow claims to have launched a 1st artificial satellite.” The very content of this front-page article was admittedly not so, dare we say, sceptical.
La Presse, owner of La Patrie for almost a quarter of a century, by the way, mentioned, in translation, that “Russia successfully launches an artificial satellite from the Earth” on its front page. Le Devoir, a well-respected Montréal daily, also featured a large article on its front page, entitled, in translation, “Russia successfully launches Earth’s first satellite.” In Québec, the most important daily in the region, Le Soleil, was sober, in translation: “Russia launches its satellite. “
You will note the use in these dailies of the term Russia, which was somewhat anachronistic given the integration of this territory into the USSR in November 1922. Anyway, let us move on.
A dispatch published that same 5 October reported that the Dominion Observatory, located in Ottawa, on the site of the Central Experimental Farm, was constantly scanning the sky for the Soviet satellite.
And yes, my reading friend, you are quite right. The Canada Agriculture and Food Museum, a sister / brother museum of the fantastic Canada Aviation and Space Museum, sits on the site of that same Central Experimental Farm.
Reverend Martin Walter Burke-Gaffney, an astronomer / mathematician / scientist at St. Mary’s University in Halifax, reported that, having followed the instructions of Soviet state broadcaster Radio Moskva, according to which the satellite was to fly over his city on 5 October, he had put a few reflector and / or refractor telescopes outside. No one had seen the smallest trace of an artificial satellite.
The leadership of the RCAF in the Atlantic Provinces reported that its radar stations had detected absolutely nothing.
During the evening of 5 October, Earl McCarron, the manager of the CHSJ radio station in St. John, New Brunswick, owned by New Brunswick Broadcasting Company Limited, itself owned by New Brunswick Publishing Company Limited, said he saw for barely a second an “orange-gold substance about the size of a fist” which emitted sparks.
With the David Dunlap Observatory having announced that it would attempt to observe the Soviet satellite during the night of 5 to 6 October, I believe, at least one reporter tried to get the results of those sightings. Total silence on the part of the astronomers.
Many Canadians scanned the skies on 6 October – and 5 October, too. In fact, people claimed to have seen “yellow balls, an orange-gold substance, round objects, streaks and flitting spheres.” If yours truly may be permitted a comment, said people demonstrated that their imagination was a tad too fertile. In fact, no observer from a Canadian observatory had yet seen the Soviet satellite. According to L’Action catholique, still as skeptical perhaps, in translation, “no scientific body in the scientific world has confirmed that it has been seen. “
Mind you, some of the people mentioned above may have seen the main stage of the Korolev R-7 “Semyorka” intercontinental ballistic missile which had put the artificial satellite into orbit. Indeed, this is precisely what was asserted, on 10 October, by A.M. Lozinski, the principal scientific collaborator of the astronomical council of the Akademiya Nauk Sovestskogo Soyuza, in other words the academy of sciences of the USSR.
As you well know, the R-7 has been mentioned several / many times in our blog / bulletin / thingee since July 2018.
According to the director of observations of the Montreal Centre of the Royal Astronomical Society of Canada, Frank J. De Kinder, said center not having telescopes designed for this type of work, it had decided not to attempt to observe the satellite. Members of the centre made that decision at a special meeting held on the evening of 6 October.
This being said (typed?), an amateur radio operator from Bathurst, New Brunswick, said he had picked up the radio signals from the Soviet satellite on 2 occasions during the evening of 6 October. Hugh McCrea was the first visually impaired amateur radio operator active in the Atlantic Provinces. Another Bathurst amateur radio operator he knew well, Garnett Wafer, said he saw “a streak in the sky that didn’t quite look like a shooting star.”
A bolt out of the blue on that same 6 October! The captain of the schooner Roden D. claimed to have seen a round, silvery object streaking at full speed over the St. Lawrence River, heading southwest, not far from Sorel, Québec, at around 6:20 p.m., local time. Having observed the flying object with the naked eye, Roger G. Desgagnés and his brother, Denis Desgagnés, hence the name of the ship, Roden D., for ROger and DENis Desgagnés, subsequently examined it with a spy-glass. These residents of Saint-Joseph-de-la-Rive, Québec, were convinced they had seen the Soviet satellite. The flying object remained visible for nearly 10 minutes.
A brief digression if I may. Renamed Monica L. in 1959, by a new owner, this ship unofficially became the schooner La Gentille of Captain Félix Joli, one of the main characters of a soap opera broadcasted between September 1963 and August 1965 by the Canadian radio and television state broadcaster, the Société Radio-Canada. Rue de l’Anse counted among its cast several of the big names in Québec theatre and television, from Maurice Beaupré to Marie Éva Lucille Gisèle Schmidt.
The Compagnie de navigation Desgagnés Limitée was / is a now defunct shipping company whose ships sailed from the Great Lakes to the Gulf of St. Lawrence. This firm should not be confused with Groupe Desgagnés Incorporée, a maritime transport company still active throughout the world in 2020, founded around 1973 by a cousin of the owners of the Roden D., Yvan Desgagnés.
Early on the morning of 7 October, an amateur radio operator from Pointe-Claire, Québec, George Good, managed to pick up the signals from the Soviet satellite. After a few minutes, a Morse code message scrambled these signals, however. When decoded, said message read as follows, “This is the man in the Moon. Better watch out or the big black bear will get you.” Good was not amused.
And yes, my reading friend who knows far too much and who could be on a spy mission, I found the mention of this message sent by a little joker in a French-language Québec daily. Specifically, I found it in an issue of L’Action catholique.
In turn, a little later in the morning of 7 October, at around 7:50 a.m., local time, 2 technicians from Canadian Marconi Company in Montréal, picked up the signals from the Soviet satellite using the powerful receivers of its laboratory.
That same 7 October, more or less at the same time, the signals of the satellite were received in the region of Québec. François Baby, one of the directors of the Centre de Québec of the Royal Astronomical Society of Canada, outside working hours of course, made a point of informing the media. To the ear, said signals sounded like the chirping of a male cricket trying to get the attention of a damsel of its species. The sounds emitted followed one another at the rate of 10 or 11 per second. The head of the Division des archives techniques of the Québec Ministère des Mines said that background noise seriously complicated the task of anyone trying to listen to the satellite’s signals.
It should be noted in passing that the 7 October edition of La Presse contained a brief, source-less article which stated that the Soviet state broadcaster Radio Moskva indicated that the artificial satellite should pass over Montréal at around 11:40 p.m., local time. Since it was only visible at dawn and / or dusk, no one would see it. This being said (typed?), pointed out the author of the article, the satellite’s radio signals could easily be picked up. The 9 October edition, for its part, mentioned the times of passage of said satellite over 8 cities in the Americas, including Ottawa, at approximately 8 a.m., local time. This information again came from the Soviet state broadcaster. On 11 October, La Presse reported that the latter had indicated that on that day said satellite was due to fly over Vancouver at around 2:50 a.m., local time, and Halifax at around 6:20 a.m., local time again.
L’Action catholique, for its part, mentioned in its 7 October edition that Radio Moskva indicated that the Soviet satellite was to fly over Québec that same day, at around 7:55 a.m., local time.
The USSR providing useful and timely information? Heaven, be still my heart! Sorry.
In a completely different vein, the 7 October edition of La Pressed reported that the Ottawa correspondent of an influential American daily, The New York Times, of New York City, New York, heard from Igor Sergeyevich Gouzenko, a former code clerk at the Soviet embassy in Canada who had defected in September 1945 with a hundred documents proving the existence of a Soviet spy network in the country.
And yes, my scholarly reading friend, the announcement of the existence of such a spy ring in February 1946 hit like a bomb. The Gouzenko affair was undoubtedly one of the triggers of the Cold War, but back to our defector / traitor to his homeland.
Gouzenko told the correspondent of The New York Times that he had just written to American President Dwight David “Ike” Eisenhower, a gentleman mentioned in several issues of our blog / bulletin / thingee since March 2018. He said he had told him that the USSR had succeeded in launching the first satellite thanks to information gathered by spies infiltrated within American firms working in the field of rocketry. Gouzenko added in his letter that said spies had sabotaged the work of said firms.
If I may be permitted a comment, one might wonder how Gouzenko, isolated in his bubble for more than 10 years, could have had access to any information on the 1950s activities of the Komitet Gosudarstvennoy Bezopasnosti or the Glavnoye Razvedyvatel’noye Upravleniye, the civil and military intelligence agencies of the USSR. That country actually did not need intelligence gathered by spies to design its aforementioned R-7 intercontinental ballistic missile. Anyway, let’s move on.
The 7 October edition of La Presse contained an editorial dedicated to the first artificial satellite. Its author began his remarks by indicating that said satellite, whose launch was scheduled as part of the aforementioned International Geophysical Year, was the most spectacular item in the list of its activities and projects, and the one most likely to interest the crowds. He went on to say that the nationality of the satellite did not matter from a scientific point of view. While it was true that the USSR preceded the United States, the latter would soon launch their own satellites, starting in the spring of 1958, following experiments carried out in the fall of 1957.
Information made public by the American authorities suggested that they were more interested in sharing the results of their research with the rest of the world than were their Soviet counterparts, who were far more secretive.
The author of the editorial pointed out that it was to the honour of science to have achieved a centuries’ old dream. The interest of the masses was mainly due to this aspect of the realisation of the USSR. For the scientific community, the putting into orbit of the Soviet satellite and, more importantly, of American satellites would make it possible to better understand the Earth and explore virtually unknown spaces.
Yours truly must admit to being a tad surprised by the tone adopted by the editorialist of La Presse. The impact of the satellite launch on the evolution of the Cold War did not seem to interest him much.
The 7 October edition of La Patrie also contained an editorial dedicated to the first artificial satellite. It profoundly differed from that of La Presse. In fact, journalist and author Conrad Langlois underlined that the launch of said satellite was of great importance from a scientific and propagandistic point of view.
The consequences of this new success in science and technology would benefit all of humanity more or less directly. “The time may not be very far away when it will be possible to go and visit the other planets,” said (typed?) Langlois, in translation. Soviet researchers had also proven that they were not lagging behind those in the United States. They could accomplish other feats before long.
If the launch of the Soviet satellite, a new stage in the history of great human achievements, was an occasion for rejoicing, the fact was that it proved once again that the struggle between free countries and the communist world was not only ideological or even military. It was and would be more and more economical, scientific and technological. The ability of the Soviet government to keep a much larger percentage of its young people in its colleges and universities than its ideological adversaries could, or wanted to, could enable the USSR to make rapid material progress. Free peoples would have to do the same before long, Langlois concluded, to prevent the communists from taking over the world without even going to war.
In his aux quatre points CARDINAUX column in the same 7 October edition of La Patrie, Dostaler O’Leary stressed that the momentous event of the launch of the Soviet satellite was going to have unexpected, if not unsuspected, consequences. The author / columnist / editor / editorialist / journalist did not seem to share the opinion of an influential and respected daily from Paris, France, and not Texas, the rather conservative Le Monde. The latter refused to give said satellite the character of a spy in orbit or of a thermonuclear weapon. Le Monde also believed that the lack of information provided before the launch suggested that the Soviet government doubted the success of the endeavour.
O’Leary agreed more with the view expressed by a fairly conservative Parisian weekly, Le Journal du dimanche. If it hoped to diminish the propaganda success achieved by the Soviet government, the only national general Sunday news weekly in France said its American counterpart would have to do everything to find something of a scientific nature whose impact on the popular imagination would be as large as that of the Soviet satellite.
O’Leary and Le Journal du dimanche evidently did not realise that the Soviet government itself was somewhat flabbergasted by the extent of the reaction to the launch of its satellite. Realising at once how much said launch could increase the prestige of the USSR, it made the conquest of space one of the hobbyhorses of its propaganda – and called for new satellite launches as soon as possible. In fact, a second satellite took off in November 1957. It carried a female dog known worldwide as Laïka – the first cosmonaut / astronaut, if I may say (type) so. This poor beast without history or pedigree died a few hours after the launch of Sputnik II.
A brief digression if I may, my reading friend. In 1944-45, the founder of Le Journal du dimanche, the famous journalist and press boss Pierre Lazareff, directed the French-speaking section of the American Broadcasting Station in Europe, a propaganda radio station established in London, United Kingdom, by the United States Office of War Information to broadcast programming into occupied Europe. One of the journalists / newsreaders who worked for him was none other than René Lévesque, a future Premier of Québec mentioned in April and September 2020 issues of our blog / bulletin / thingee, but back to our story.
Again and again this eternal 7 October, 5 people, 5 white men more precisely, including the Prime Minister of Canada, receive an honorary doctorate from McGill University in Montréal. During his acceptance speech on the occasion, as part of founders’ day celebrations, John George Diefenbaker said that the free world should not be afraid to “acknowledge this triumph of technology and pay tribute where it [was] due.” In fact, he added, he would not be surprised to learn in the more or less distant future that one of the young people in front of him was travelling in space.
This being said (typed?), Diefenbaker pointed out how challenging the launch of the Soviet satellite was for the free world, especially the countries of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization, including Canada. It should not be forgotten that the ultimate goal of the government of the USSR was to dominate all of humanity.
According to some sources, Diefenbaker recalled, there were more people with science degrees in the USSR than in all the countries of the free world combined. While resorting to the methods used by the Soviet government was out of the question, free countries should nevertheless work together to provide more dough / moolah, my words and not those of the Prime Minister, to the scientific community. A futile desire to save a few pennies should not endanger the survival of the free world.
As the daytime of 7 October drew to a close, staff at the David Dunlap Observatory attempted to pick up radio signals from the artificial satellite as it flew over Toronto. The eminent and respected director of this institution of high learning, no pun intended, John Frederick Heard, reported that he had heard nothing. No one had heard anything satellite-ish, in fact. Heard said the Soviet satellite’s radio equipment might have broken down. It might also have been transmitting on another frequency by then.
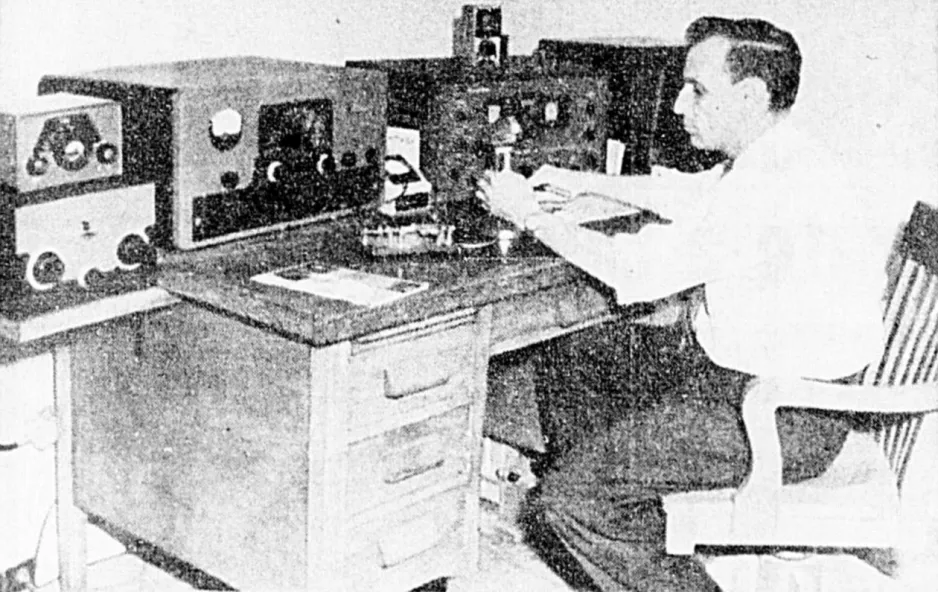

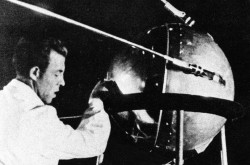
Amateur radio operator Gilles Blackburn with his equipment, Chicoutimi, Québec. Albert Tremblay, “Le signal du satellite capté à Chicoutimi.” Le Progrès du Saguenay, 9 October 1957, 1.
In Chicoutimi, a city now integrated into the city of Saguenay, Québec, amateur radio operator Gilles Blackburn was far more fortunate. This regional director of the Québec association of radio amateurs, Radio Amateur du Québec Incorporée, and president of the Club des sans-filistes amateurs de Chicoutimi Incorporée, in fact picked up the signals from the Soviet satellite on 2 occasions during the evening of 7 October, at approximately 7:05 p.m. and 8:45 p.m., local time. Blackburn was an employee of the Compagnie électrique du Saguenay, a utility company in the Saguenay region.
A few other amateur radio operators from the same region, including Gérard Duchesne, one of the directors of the Club des sans-filistes amateurs de Chicoutimi, also managed to hear said signals. At least one recorded them. Blackburn contacted him so that Albert Tremblay, the reporter for Le Progrès du Saguenay of Chicoutimi, Québec, who was at his home, could hear them.
Early on the morning of 8 October, Blackburn contacted an amateur radio operator in Paris, France. This good buddy told him that he too had picked up the signals from the Soviet artificial satellite.
And it is with these few words that the first part of this article of our blog / bulletin thingee dedicated to World Space Week 2020 ends. Do not forget to come back to this site next week to read the second one.









































![A block of photographs showing some of the people involved in the bombing of beluga whales in the estuary and gulf of the St. Lawrence River. Anon., “La chasse aux marsouins [sic]. » Le Devoir, 15 August 1929, 6.](/sites/default/files/styles/thumbnail_7/public/2024-09/Le%20Devoir%2015%20aout%201929%20page%206.jpg?h=584f1d27&itok=TppdLItg)



























































































































































































![Peter Müller at the controls [sic] of the Pedroplan, Berlin, Germany, March 1931. Anon., “Cologne contre Marseille – Le mystère du ‘Pédroplan.’ [sic]” Les Ailes, 2 April 1931, 14.](/sites/default/files/styles/thumbnail_7/public/2021-04/Les%20Ailes%202%20avril%201931%20version%20big.jpg?h=eafd0ed4&itok=WnBZ5gMf)












![One of the first de Havilland Canada Chipmunk imported to the United Kingdom. Anon., “De Havilland [Canada] DHC-1 ‘Chipmunk.’” Aviation Magazine, 1 January 1951, cover.](/sites/default/files/styles/thumbnail_7/public/2021-01/Aviation%20magazine%201er%20janvier%201951%20version%202.jpg?h=2f876e0f&itok=DM4JHe5C)