Magnetron
This article was originally written and submitted as part of a Canada 150 Project, the Innovation Storybook, to crowdsource stories of Canadian innovation with partners across Canada. The content has since been migrated to Ingenium’s Channel, a digital hub featuring curated content related to science, technology and innovation.
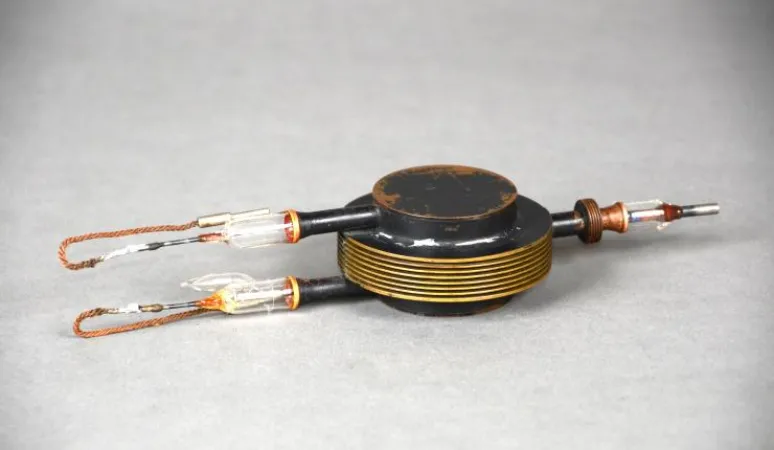
The magnetron helped the Allies fight the Second World War.
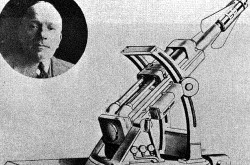
The magnetron gave the Allies radar superiority in the Second World War. Radar, which researchers had developed before the war, uses radio waves to detect and track objects like ships and aircraft. It works by transmitting radio waves out into the atmosphere and then reading the signals that bounce off objects in the area. These signals give operators range and bearing and, over time, let them track a moving object’s direction and speed. The magnetron generated high-powered pulses of microwaves that provided higher resolution and greater directionality — and therefore greater range — than systems using longer waves. It also reduced the size of equipment, which was especially important for airborne radars. Henry Boot and John Randall of Birmingham University in England invented the magnetron in 1940 and General Electric manufactured this one the same year. A British technical mission brought it to North America in 1940, leaving it in Canada after having used it to help persuade a reluctant government to join the Allied radar research and production effort.
The word radar is an acronym derived from RAdio Detection And Ranging.