Harold Elford Johns, 1915–1998
This article was originally written and submitted as part of a Canada 150 Project, the Innovation Storybook, to crowdsource stories of Canadian innovation with partners across Canada. The content has since been migrated to Ingenium’s Channel, a digital hub featuring curated content related to science, technology and innovation.
Harold Johns developed powerful new radiation instruments to treat cancer — finding peacetime uses for wartime nuclear technology.
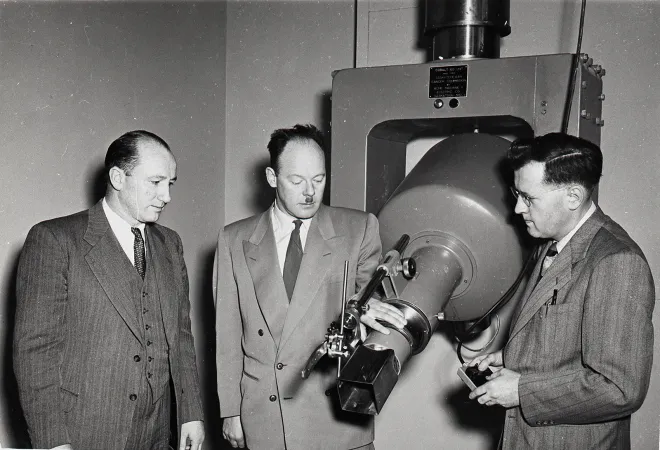
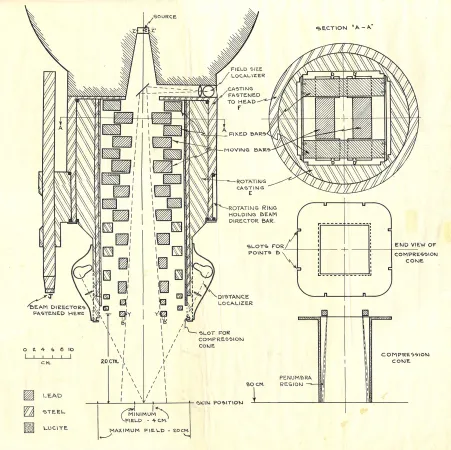
Harold Elford Johns introduced high-energy radioactive isotopes into cancer treatment, helping to pioneer the field of nuclear medicine. Previous radiation treatments had proven ineffective, leaving cancer patients with burns and other medical complications. Johns, who joined the University of Saskatchewan’s physics department — and the province’s new Cancer Commission—in 1944, realized the high-energy x-rays could kill deeply buried cancerous cells. Working with graduate students and colleagues such as Sylvia Fedoruk, Johns proposed using a radioactive isotope called cobalt-60, which emitted powerful gamma rays. Johns worked with Saskatoon machinist John MacKay to produce a prototype machine that used cobalt-60 from Atomic Energy of Canada Limited’s NRX reactor in Chalk River, Ontario. In November 1951, the machine treated its first cancer patient in Saskatoon. Another medical research group based in London, Ontario, developed a similar machine that treated cancer patients the same year. Johns also contributed to the development of CT scanners, mammographic imaging, and to research on the effects of ultraviolet rays on DNA.
Johns was born in China, where his parents worked as missionaries. After completing work on cobalt-60 therapy, he moved to Toronto in 1956 to head the Physics Division at the Ontario Cancer Institute. He also joined the University of Toronto and was instrumental in creating the school’s medical biophysics program.