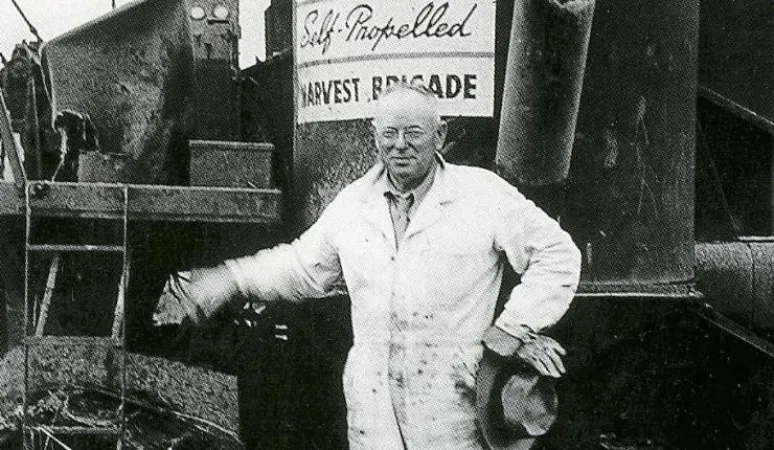
Tom Carroll, Massey-Harris Engineer: Building a Better Harvester
This article was originally written and submitted as part of a Canada 150 Project, the Innovation Storybook, to crowdsource stories of Canadian innovation with partners across Canada. The content has since been migrated to Ingenium’s Channel, a digital hub featuring curated content related to science, technology and innovation.
In 1936, Tom Carroll and a team of researchers with Massey-Harris Canada (now Massey Ferguson) in Ontario began work on a revolutionary new combine harvester. Earlier versions of the combine used horse or tractor power to pull the machine through the fields. The new and affordable combine was self-propelled, reducing the cost of fuel and labour needed to bring in a harvest.
With the Second World War on the horizon, the MH-20 was rushed into production. The first self-propelled Massey-Harris combines hit the market in early 1939 and were an instant commercial success.
Wartime metal shortages put Massey-Harris in jeopardy, until an enterprising sales manager proposed an ambitious project. If the governments of Canada and the United States would allow the production of 500 new MH-21 harvesters, the company would sell only to farmers willing to join a “Harvesting Brigade”. By bringing large-scale harvest automation to a multitude of smallholders across North America, the scheme was designed to save fuel, free up thousands of tractors and labourers, and harvest crops that might have otherwise gone to waste for lack of resources. Not coincidentally, the project also gave the company unprecedented exposure to the North American marketplace. The Brigade began work in the southern United States in late spring 1944 and moved north to finish the harvest on the Canadian Prairies in the fall.
The 1944 Harvesting Brigade was a huge success, delivering 25 million bushels of grain, and saving about 333,000 hours of labour and 500,000 gallons of fuel. The operation was repeated in 1945.