Flipping the switch
This article was originally written and submitted as part of a Canada 150 Project, the Innovation Storybook, to crowdsource stories of Canadian innovation with partners across Canada. The content has since been migrated to Ingenium’s Channel, a digital hub featuring curated content related to science, technology and innovation.
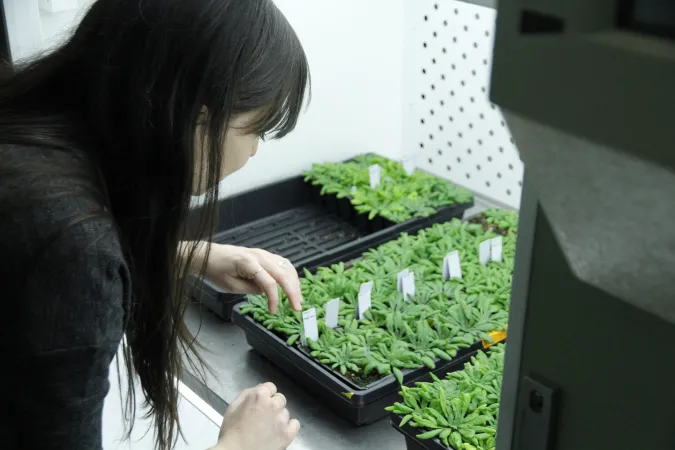
Researchers at the Sainsbury Laboratory, including Canadian biologist Jacqueline Monaghan, have uncovered a previously unknown means by which plants are able to regulate how their immune systems respond to pathogens. A group of small peptides, referred to as RALFs (Rapid ALkalinization Factors), serve to dampen immune signaling – preventing further response once the infection has been dealt with by the plant’s immune system. The finding could pave the way to improve the immune systems of food crops, which would have a tremendous impact on food security.
Dr. Monaghan, now a professor of biology at Queen’s University, explains how the team examined how plant immune systems work to respond to threats, as well as how plants regulate their pathogen responses in order to avoid negative impacts to their growth and development.
“Most people are familiar with their own immune system and how it functions, but we don’t often consider immune systems in other organisms,” explains Dr. Monaghan, who took part in the study while a postdoctoral researcher at the Sainsbury Laboratory. “Immune responses need to be ‘turned off’ once the threat is eliminated – otherwise, there can be negative effects on the organism. In humans, this can result in autoimmune disorders. In plants, we see stunted growth and other detrimental effects.”
Dr. Monaghan and her colleagues measured this response by first tracking the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) – chemically reactive compounds – produced in plants exposed to molecules known to elicit an immune response. The plants were also infected with various pathogens and the immune response was tracked. Genetic tests allowed the researchers to identify a number of genes that are important for these immune responses. The results of the study expand the understanding of how plants are able to fight off diseases – possibly serving as a stepping-stone to future research that could improve immune response and food crop yields.
Dr. Monaghan says that this research plays a role in furthering the collective understanding of how plants respond to environmental threats and pathogens. She says that future developments could lead to improving the immune systems of food crops, which would have a tremendous impact on food security.
“Studies such as ours, which aim to understand the fine details of plant immunity, make incremental progress towards that capability,” she explains. “If you increase immunity broadly in crops, you’ll have a decrease in yield – the plants may be stunted because they’re constantly prepared to fight infection, rather than growing. We need to understand that balance so that we can improve the immune response in crops, without those detrimental effects. Knowing how to ‘flip that switch’ is key.”
The full study, titled The receptor kinase FER is a RALF-regulated scaffold controlling plant immune signaling, was published in the journal Science.