A pioneer in plant breeding
This article was originally written and submitted as part of a Canada 150 Project, the Innovation Storybook, to crowdsource stories of Canadian innovation with partners across Canada. The content has since been migrated to Ingenium’s Channel, a digital hub featuring curated content related to science, technology and innovation.
Shawna O’Neill
Algonquin College Journalism Program
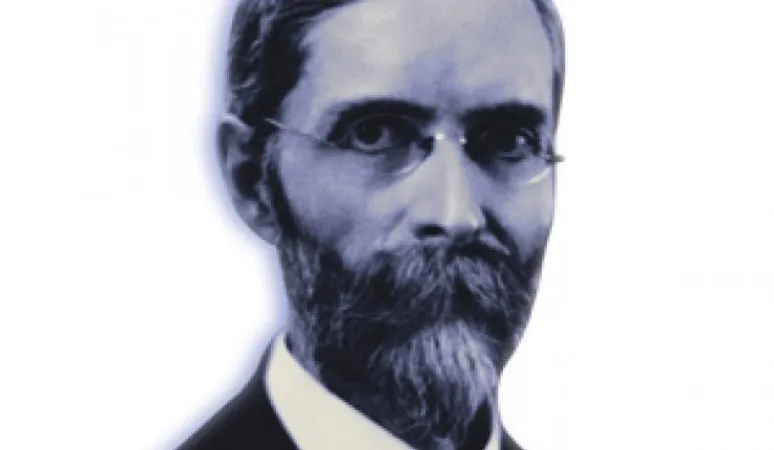
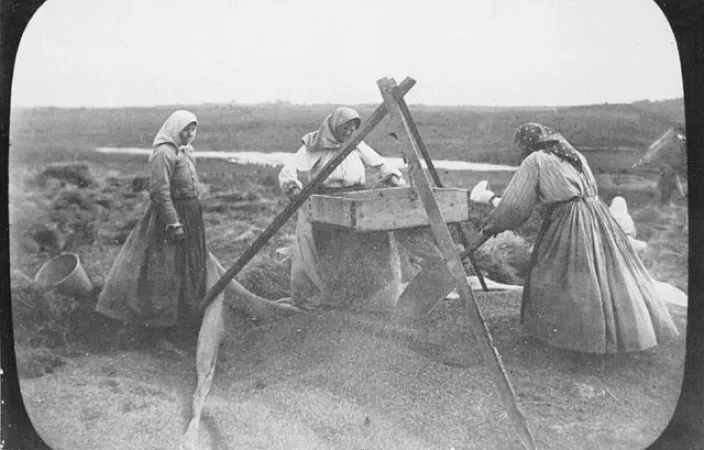
Sir Charles Edward Saunders is credited for breeding the most popular strain of wheat in Canada: Marquis Wheat. This early-ripening durable wheat allowed farmers to grow farther north, leading to Canada’s reputable hard spring wheat. Derived from a cross between two wheats: Hard Red Calcutta and Red Fife, the Marquis Wheat was meticulously crafted by Saunders after a couple years of research and growing. At the time, plant breeding was a completely new kind of science.
Saunders, a chemistry professor who graduated from the University of Toronto, would chew the kernels to determine which lines had strong gluten. Marquis became the supreme wheat of all cross bread wheat. Bulk seed was sent to Indian Head, Sask., for further testing starting in 1907. By the 1920s’ 90 per cent of the 17 million acres of wheat in western Ontario was Marquis.
Saunders, born in London, Ont., earned his degree from the University of Toronto, and a PhD from the Johns Hopkins University. In 1902 he moved to Ottawa to work at the central experimental farm. His father, William Saunders, originally established experimental farms in Canada, which led to Saunders’ investment in wheat development. In 1921 he was made a Fellow of the Royal Society of Canada and received an honorary Doctor of Laws from the University of Western Ontario. In 1925 he was awarded an honorary doctorate from the University of Toronto and the Flavelle Medal for Science from the Royal Society of Canada.
Saunders died in 1937. He was inducted into the Canadian Science and Engineering Hall of Fame in 1999.