A Bomb that Cures
This article was originally written and submitted as part of a Canada 150 Project, the Innovation Storybook, to crowdsource stories of Canadian innovation with partners across Canada. The content has since been migrated to Ingenium’s Channel, a digital hub featuring curated content related to science, technology and innovation.
For more than half a century, Canada’s National Research Council (NRC) has been a leader in cancer research. In the early 1950s, the cobalt-60 bomb treatment launched a new era in cancer therapy that has saved millions of people around the world. Since then, NRC researchers have continued to advance the field of radiation therapy.
In the 1940s, only about one in five people who got cancer survived for more than five years. Patients’ prospects improved greatly after two Canadian doctors asked NRC for radioactive cobalt to treat patients. NRC fulfilled this request by producing the cobalt-60 isotope at its nuclear reactor in Chalk River, Ontario. Soon, survival rates for some cancers went from 25 to 75 per cent. Today, Chalk River is the world’s largest producer of medical isotopes, used to treat more than 20 million people in 80 countries each year.
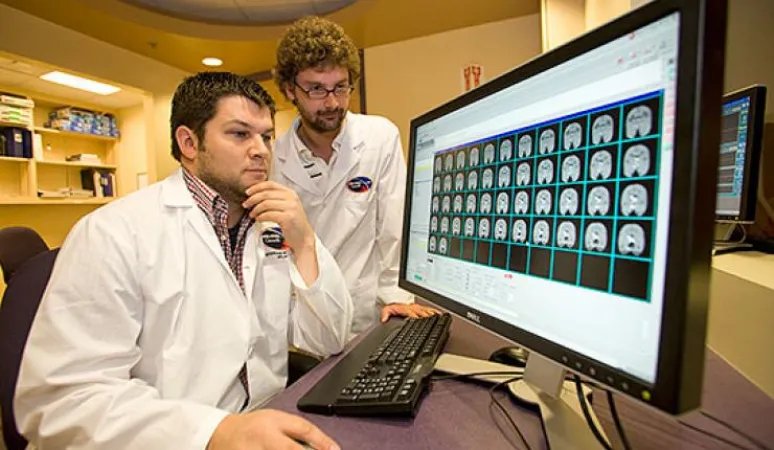
Meanwhile, NRC has also simplified the radiation therapy process. To ensure that only cancerous tissue is destroyed, medical physicists must determine the precise dose of radiation needed. This calculation takes hours, but NRC scientists have developed a revolutionary way to target tumours in minutes. Their innovative desktop software program considers a patient’s anatomy, the size and depth of the cancer, and other key details. The program was licensed for commercial use in 2000 and NRC continues to train medical physicists from abroad to calculate radiation doses.