Highlights:
- A biplane designed in the U.K. in 1932, as a light, compact, economic and reliable passenger aircraft
- After the Second World War, Canadian Fox Moths were built with either skis or floats, for use as bush planes
- Developed between two significant eras in Canada's aviation history: the bush-flying period and the early days of passenger airlines
- First flight was in 1932
Image Gallery:
History:
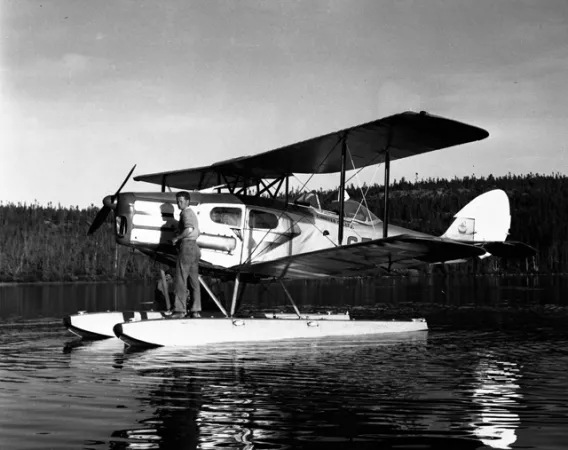
The Fox Moth was designed in England in 1932 as a light, economic transport, and was built using as many Tiger Moth components as possible. Fox Moths were produced in Canada after the Second World War mainly to keep the plant in production, but also to satisfy the increasing need for new bush aircraft. All the Canadian modifications made to the Tiger Moth were also applied to the Fox Moth. Of the 53 produced, 39 remained in Canada, most of which were operated in float/ski configuration, and gave years of satisfactory service.
The Fox Moth, though efficient, was a bit of an anachronism. For example, a modern, moulded- plexiglas sliding cockpit-hood was attached to what was essentially a 1932 aircraft. Communication between the passenger cabin in the fuselage and the cockpit to the rear was through a hole in the instrument panel. De Havilland designed a special stretcher for the Fox Moth, in order that it could operate as an air ambulance.
Current Location:
Airlines Exhibition, Canada Aviation and Space Museum
Provenance:
Donation from Maxwell Ward
Built in Canada in 1947, this Fox Moth was owned by a number of operators before Maxwell Ward (founder of Wardair Inc., a private Canadian airline company) purchased it in the 1980s. Ward had the aircraft repainted to match the markings of his first bush plane (a de Havilland Fox Moth that he had bought in 1946 and used for several years until it was destroyed in a crash in the 1950s). Ward restored this Fox Moth and presented it to the Museum in 1989.
Technical Information:
| Wing Span | 9.4 m (30 ft 10 3/5 in) |
| Length | 8.2 m (26 ft 9 in) |
| Height | 2.7 m (8 ft 9 1/2 in) |
| Weight, Empty | 655 kg (1,445 lb) |
| Weight, Gross | 1,045 kg (2,300 lb) |
| Cruising Speed | 135 km/h (84 mph) |
| Max Speed | 154 km/h (96 mph) |
| Rate of Climb | 135 m (450 ft) /min |
| Service Ceiling | 3,353 m (11,000 ft) |
| Range | 528 km (328 mi) |
| Power Plant | one de Havilland Gipsy Major 1C, 145 hp, inverted in-line engine |
- View all the collection highlights at the Canada Aviation and Space Museum
- View other collection highlights related to Aviation