Highlights:
- An ultra-light monoplane designed in 1929 by Jean A. Roché and built in the U.S. by Aeronautical Corporation of America (Aeronca)
- Designed as a cheap and simple flying machine for the amateur pilot; credited as triggering an American boom in light aircraft
- Appeared during the Depression and its relatively low price made it a popular civilian aircraft
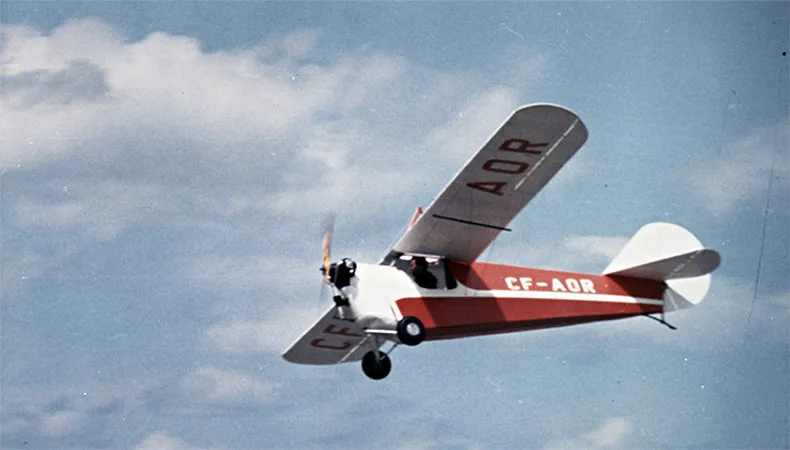
- Known as "the flying bathtub" due to its unusual shape; its steel tube fuselage and its wooden wings were covered with doped cotton fabric
- First C-2 in Canada was displayed at a Montreal air meet in 1930
- First flight was on October 20, 1929
Image Gallery:
History:
The C-2 was designed to be a cheap and simple flying machine for the amateur pilot. Built at the beginning of the Great Depression, it appealed to those who could not afford larger more expensive airplanes because of its relatively low price. After the C-2 appeared at a Montreal air meet in 1930, the Aeronautical Corporation of Canada was formed in Toronto. This company imported and sold 17 C-2s and C-3s during the 1930s. Approximately 515 C-2s and C-3s had been made when production stopped in 1937.
A C-2 was flown higher than 6 000 m (20 000 ft), and one fitted with special fuel tanks remained aloft for 26 hours. The C-2 was dubbed the "flying bathtub" due to its unusual fuselage contour.
Current Location:
Reserve Hangar, Canada Aviation and Space Museum
Provenance:
Purchase
Manufactured in 1931, the Museum's aircraft was the eighth C-2 built by Aeronca. It was originally sold to G. A. Dickson of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania; it then passed through the hands of several owners. A more powerful engine was installed prior to the Museum acquiring it in 1967. The Museum replaced the original vertical tail with that of a late-production C-3.
Technical Information:
Scroll to the right to view more of the table.
| Wing Span | 11 m (36 ft) |
| Length | 6.0 m (20 ft) |
| Height | 2.3 m (7 ft 6 in) |
| Weight, Empty | 184 kg (406 lb) |
| Weight, Gross | 317 kg (700 lb) |
| Cruising Speed | 105 km/h (65 mph) |
| Max Speed | 129 km/h (80 mph) |
| Rate of Climb | 137 m/min (450 ft) |
| Service Ceiling | 5,030 m (16,500 ft) |
| Range | 322 km (200 mi) |
| Power Plant | one Aeronca E-113, 36 hp, horizontally opposed engine |
- View all the collection highlights at the Canada Aviation and Space Museum
- View other collection highlights related to Aviation