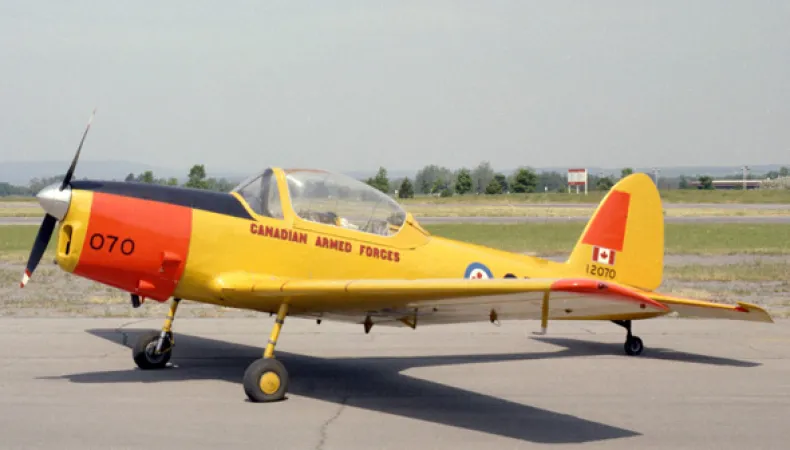
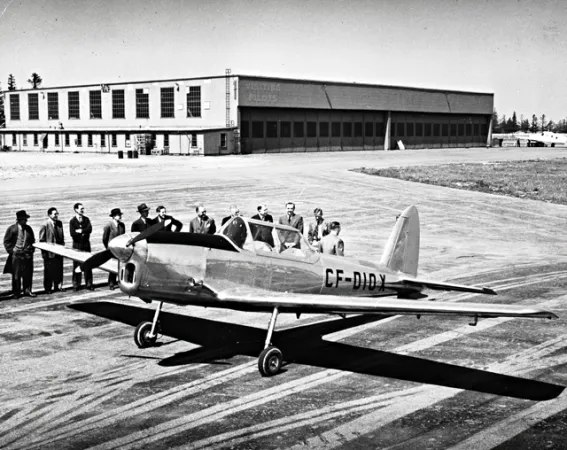
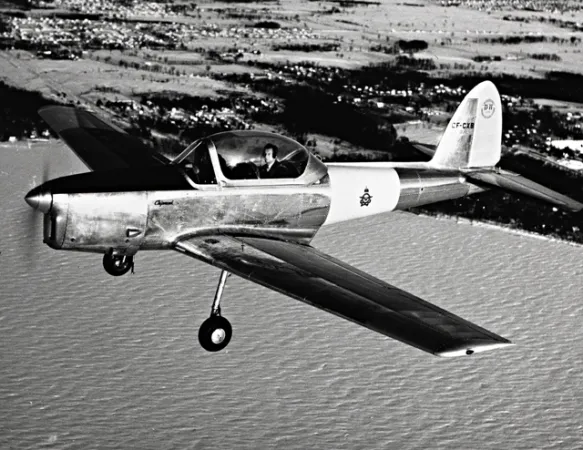
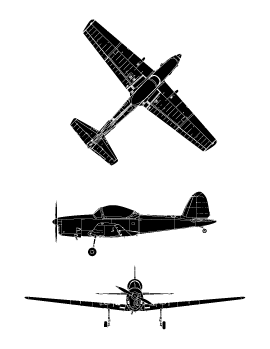
Highlights:
- A training aircraft developed for the RCAF and RAF at the end of the Second World War; designed as the successor to the de Havilland Tiger Moth, an earlier (British) training aircraft
- First of many de Havilland Canada aircraft to be named after North American wildlife
- First Canadian-designed aircraft to be manufactured abroad; far more were built overseas than in Canada
- Attracted publicity after HRH Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh, trained on the aircraft in 1952
- Frequently flown by U.S. aerobatic pilot Arthur Scholl during international air shows
- First flight was on May 22nd, 1946
Image Gallery:
History:
When the RCAF began to expand in the late 1940s, both elementary and advanced pilot-training depended upon the North American Harvard. It was soon recognized that a simpler aircraft was required for elementary pilot-training. The Chipmunk was chosen for this role. Many of the 217 Chipmunks made in Canada went to the RCAF, but Canadian Chipmunks were also sent to Egypt, Lebanon, and Thailand. Britain made 1 000 Chipmunks and Portugal, 66, under licence.
The Chipmunk was the first Canadian-designed aircraft to be made abroad under licence. Some civilian Chipmunks have been provided with more powerful engines to enhance their aerobatic capability and have been used in international aerobatic competitions.
Current Location:
Reserve Hangar, Canada Aviation and Space Museum
Provenance:
Purchase
Built in 1956, this aircraft was the 207th Chipmunk built in Canada and was one of the last Chipmunks produced in the country. It was used for training by the RCAF in Centralia and Dunville, Ontario; Portage la Prairie, Manitoba; and Saskatoon, Saskatchewan. This Chipmunk was put in storage in the Aerospace Maintenance Depot Unit in Mountain View, Ontario in 1971 and was purchased by the Museum the following year. It was given the civilian identity CF-CIA for its flight to Rockcliffe airport.
Technical Information:
| Wing Span | 10.5 m (34 ft 4 in) |
| Length | 7.7 m (25 ft 5 in) |
| Height | 2.1 m (7 ft) |
| Weight, Empty | 544 kg (1,199 lb) |
| Weight, Gross | 875 kg (1,930 lb) |
| Cruising Speed | 200 km/h (124 mph) |
| Max Speed | 225 km/h (140 mph) |
| Rate of Climb | 275 m (900 ft) /min |
| Service Ceiling | 5,240 m (17,200 ft) |
| Range | 451 km (280 mi) |
| Power Plant | one D.H. Gipsy Major 10, 145 hp, inverted in-line engine |
- View all the collection highlights at the Canada Aviation and Space Museum
- View other collection highlights related to Aviation